Question 1. Choose the correct option from the bracket and explain the statement giving reasons:
(Oxidation, displacement, electrolysis, reduction, zinc, copper, double displacement, decomposition)
(a)To prevent rusting, a laver of ……… metal is applied on iron sheets.
Answer: To stop rusting, a coating of zinc metal is applied on iron sheets. Because of corrosion, an iron deposit is formed rusting of iron is an oxidation process. This substance is known as rust. To avoid corrosion iron sheets are covered with zinc metal.
b. The conversion or ferrous sulphate to ferric sulphate is ……..reaction.
Answer: When ferrous sulphate is converted into ferric sulphate it is an oxidation reaction. The positive charge is increased by one unit when the ferric ion is formed from a ferrous ion when the ferrous ion loses one or more electrons is known as oxidation.2FeSO4 →Fe2(SO4)3
Fe2 + SO42- → 2Fe3+ + SO42-
c. When an electric current is passed through acidulated water _____ of water takes place.
Answer: The decomposition of water takes place when an electric current is passed through acidulated water during this reaction hydrogen and oxygen gas is formed
Answer: When an electric current is passed through acidulated water decomposition of water takes place. In this reaction. hydrogen and oxygen gas are formed. Decomposition happens because of electric current, this is also known as electrolytic decomposition.
Question 2. Write answer to the following Questions.
a. What is the reaction called when oxidation and reduction take place simultaneously? Explain with one example.
Answer. When oxidation and reduction take place at the same time is known as an oxidation-reduction reaction or redox reaction in this reaction one gets oxidised while the other gets reduced Redox reaction = Reduction + Oxidation. In a redox reaction, the reductant is oxidized by oxidant and the oxidant is reduced by the reductant.
Example: CuO(s) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + H2O
In this reaction, reduction takes place as oxygen is removed from copper oxide so it is a reduction of CuO, on other hand oxygen is accepted by hydrogen to form water which means oxidation of hydrogen happens. In such a way oxidation and reduction happens at the same time.
b. How can the rate of the chemical reaction, namely, the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide be increased?
Answer: Hydrogen peroxide decomposes into the water very slowly at room temperature, on the other hand when manganese dioxide is added the same reaction happens very fast.
c. Explain the term reactant product giving examples.
Answer:
- The substance that participates in a chemical reaction is called a reactant and this substance undergoes bond braking.
- Because of chemical reactions substances are formed and in this bond are formed and is called products.
- Example:During a chemical reaction, carbon dioxide gas is produced when coal burns in the presence of air. The reactants in this reaction are coal (carbon) and oxygen (from the air), while the product is carbon dioxide.
d. Explain the types of reactions concerning oxygen and hydrogen. Illustrate with examples.
Answer: There are two types of reactions concerning oxygen and hydrogen.
- Oxidation reaction
- Reduction reaction.
1. Oxidation reaction:
Examples:
(1) Carbon dioxide is formed when carbon burns in the air, which means carbon accepts oxygen hence it is an oxidation reaction.
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
(2) Hydrogen gas is formed when sodium reacts with ethyl alcohol, which means that hydrogen gas is removed from ethyl alcohol and this is called an oxidation reaction
2. Reduction reaction:
Examples:
(1) A reddish layer of copper is formed when hydrogen gas is passed over a copper oxide in such a reaction an oxygen atom is removed from Cuo to form copper hence it is a reduction.
(2) Methane is obtained when hydrogen gas is passed over hot coke means hydrogen is added to coke Hence, this is a reduction.
e. Explain the similarity and difference in two events, namely adding NaOH to water and adding CaO to water.
Answer: Similarity: When NaOH and Cao are dissolved in water separately solid NaOH dissolves and produces heat and as a result, the temperature increases so this is an exothermic reaction. Ca(OH)2 is formed When solid CaO is dissolved in water, and a huge amount of heat is released this is also an exothermic both reactions are combination reaction. NaOH(s) + H2O → NaOH(aq) + Heat
CaO(s) + H2O → Ca(OH)2(aq) + Heat
Difference:
- NaOH which is an Aqueous solution is considered as a strong alkali.
- Ca(OH)2 Aqueous solution is considered as a weak alkali.
- Question Explain the following terms with examples.
a. Endothermic reaction
Answer: Endothermic reaction: In this reaction heat is absorbed and is called an endothermic reaction when KNO3(s) dissolves in water, the temperature of the solution falls as heat is absorbed during the reaction.
KNO2(s) + H2O(l) + Heat → KNO3(aq) - Combination Reaction: A single product is formed when two or more reactants combine and is called a combination reaction.
Examples:
1. Hydrogen chloride gas reacts with ammonia gas and creates salt in a gaseous state and in no time, it condenses and turns into a solid state at room temperature.
2. Magnesium burns in air to form white powder of magnesium oxide as a single product.
3. Iron reacts with sulphur to form iron sulphide.
c. Balanced equation
Answer: A reaction in which the number of atoms of an element in reactants is equal to the product of a reaction is called the Balanced equation in which several atoms of the element is the same at the reactant and product side.
Example: AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3
d. Displacement reaction:
Answer: The reaction in which a more reactive element takes the place of an ion of a less reactive element means a more reactive ion of an element replaces an ion of a less reactive element this reaction is known as displacement reaction. When zinc granules is added to copper sulphate solution the zinc ions formed from zinc atoms take the place of Cu2+ ions in CuSO4, and copper atoms, formed from Cu2+ ions come out i.e. the more reactive zinc displace the less reactive Cu from copper sulfate
4. Give scientific reason:
a. When the gas formed on the heating limestone is passed through freshly prepared lime water, the lime water turns milky.
Answer: When limestone is heated, it produces calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide gas is then passed through recently made lime water, resulting in the formation of insoluble calcium carbonate and water. This causes the lime water to become cloudy.
b. It takes time for pieces of Shahabad tile to disappear in HCl, but its powder disappears rapidly.
Answer: The reaction rate is influenced by the size of the particles involved in the reaction. Smaller particles result in increased total surface area and a faster reaction rate. When dilute HCl reacts with pieces of Shahabad tile, CO2 effervescence is generated and the tile slowly disappears. Conversely, CO2 effervescence occurs more rapidly when reacting with Shahabad tile powder, causing it to vanish quickly.
c. While preparing dilute sulphuric acid from concentrated sulphuric acid in the laboratory, the concentrated sulphuric acid is added slowly to water with constant stirring.
Answer: (1) The process of creating diluted sulfuric acid involves an extremely heat-releasing reaction.
(2) To make diluted sulfuric acid, a large amount of water is placed in a glass container surrounded by ice and cooled for twenty minutes. Then, a small amount of concentrated H2SO4 is gradually added with stirring, releasing heat in small increments to produce the diluted sulfuric acid.
(3) Conversely, when diluting concentrated sulfuric acid with water, a significant amount of heat is released, causing rapid evaporation of the water. This can lead to a potential accident if the water is poured into the concentrated H2SO4.
d. It is recommended to use an airtight container for storing oil for a long time.
Answer: (1) When edible oil is left for a prolonged period, it oxidizes upon exposure to air, resulting in rancidity and a change in its odour and flavour.
(2) To prevent rancidity in food cooked in oil or ghee, antioxidants are used. Storing the food in an airtight container can also slow down the oxidation process.
Question 5.
Observe the following picture a write down the chemical reaction with an explanation.
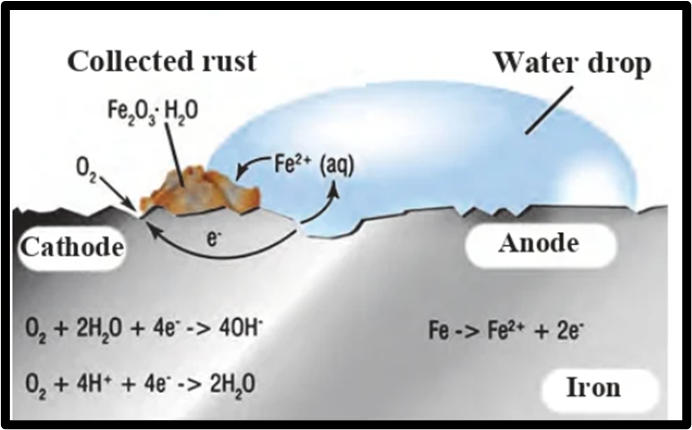
Answer: The rusting of iron is a type of oxidation, but it is not a simple reaction between oxygen and the iron surface. Instead, it involves an electrochemical process where different areas on the iron surface become either anode or cathode. At the anode, Fe is oxidized to Fe2+, while at the cathode, O2 is reduced to create water. As Fe2+ ions move away from the anode, they react with water and undergo further oxidation to produce Fe3+ ions, which then combine with water to create a reddish-colored hydrated oxide known as rust. This corrosion of iron is caused by various elements in the atmosphere that lead to the oxidation of metals and ultimately result in their deterioration.
Question 6.
Identify from the following reactions the reactants that undergo oxidation and reduction.
a. Fe + S → FeS
Answer:
Fe + S → FeS
In this reaction, Iron (Fe) undergoes oxidation
and sulphur. (S) undergoes reduction.
b. 2Ag2O → 4Ag + O2↑
Answer:
2Ag2O → 4Ag + O2↑
In this reaction, reduction of Ag2O takes place.
c. 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
Answer:
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
In this reaction, oxidation of Mg takes place.
d. NiO + H2 → Ni + H2O
Answer:
NiO + H2 → Ni + H2O
In this reaction, reduction of NiO takes place and oxidation of H2 takes place.
Question 7.
Balance the following equation stepwise.
a. H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) → H2SO4(l)
Answer:
Step 1: Rewrite the given equation as it is
H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) → H2SO4(l)
Step 2: write the number or atoms of each element in the unbalanced equation on both sides of equations.
| Element | Number of atoms in reactant (left side) | Number of atoms in products (right side) |
| H | 4 | 2 |
| S | 2 | 1 |
| O | 8 | 4 |
Step 3: To equalise the number of hydrogen atoms, sulphur atoms and oxygen atoms we use 2 as the coemficient or factor in the product.
| Element | Number of atoms in reactant (left side) | Number of atoms in products (right side) |
| H | 4 | 2 × 2 |
| S | 2 | 1 × 2 |
| O | 8 | 4 × 2 |
| Total | 14 | 14 |
Now the equation becomes H2S2O7 + H2O → 2H2SO4
Now, count the atoms of each element on both sides of the equation. The number of atoms on both sides are equal. Hence, the balanced equation is
H2S2O7 + H2O → 2H2SO4
Now indicate the physical states of the reactants and products.
H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) → 2H2SO4(l)
b. SO2(g) + H2S(aq) → S(s) + H2O(l)
Answer:
Step 1:
Rewrite the given equation as it is
SO2(g) + H2S(aq) → S(s) + H2O(l)
Step 2:
Write the number of atoms of each element in the unbalanced equation on both sides of equations.
| Element | Number of atoms in reactants (left side) | Number of atoms in products (right side) |
| S | 2 | 1 |
| O | 2 | 1 |
| H | 2 | 2 |
The number of hydrogen atoms on both sides of the equation is same, therefore, equalise the number of sulphur atoms and oxygen atoms.
Step 3: To balance the number of sulphur atoms:
| Number of atoms of sulphur | In reactants | In products | |
| S2O | H2S | (S) | |
| Initially | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| To balance | 1 | 1 | 1 × 2 |
To equalise the number of sulphur atoms, we use 2 as the factor in the product, now the equation becomes
SO2 + H2S → 2S + H2O
Step 4:
To equalise the number of oxygen atoms in the unbalanced equation.
| Number of atoms of oxygen | In reactants (SO2) | In products H2O |
| Initially | 2 | 1 |
| To balance | 2 | 1 × 2 |
To equalise the number of sulphur atoms, we use 2 as the factor in the product i.e. H2O, now the unbalanced equation becomes
SO2 + H2S → 2S + 2H2O
Step 5:
To equalise the number of hydrogen atoms in unbalanced equation:
| Number of atoms of hydrogen | In reactants (H2S) | In products (H2O) |
| Initially | 2 | 4 |
| To balance | 2 × 2 | 4 |
To equalise the number of hydrogen atoms we use 2 as the factor in the reactant i.e, H2S, now the unbalanced equation become
SO2 + 2H2S → 2S + 2H2O
Now, count the atoms of each element on both sides of the equation, there are less number of sulphur atoms in the product. Now equalise the sulphur atoms, the balanced equation becomes,
SO2 + 2H2S → 3S + 2H2O
Now indicate the physical states of reactants and products.
SO2(g) + 2H2S(aq) → 3S(s) + 2H2O(l)
c. Ag(s) + HCl(l) → AgCl ↓ + H2 ↑
Answer:
Step 1:
Rewrite the given equation as it is
Ag(s) + HCl(l) → AgCl ↓ + H2 ↑
Step 2:
write the number of atoms or each element in the unbalanced equation on both sides of equations.
| Element | Number of atoms in reactants (left side) | Number of atoms in products (right side) |
| Ag | 1 | 1 |
| H | 1 | 2 |
| Cl | 1 | 1 |
The number of silver and chlorine atoms on both sides of the equation are same, therefore, equalise the number of hydrogen atoms.
Step 3:
To balance the number of hydrogen atoms.
| Number of atoms of hydrogen | In reactants HCl | In products H2 |
| Initially | 1 | 2 |
| To balance | 1 × 2 | 2 |
To equalise the number of hydrogen atoms, we use 2 as the factor in the product HCl, now the unbalanced equation become
Ag(s) + 2HCl → AgCl + H2
Step 4:
To balance the number of chlorine atoms:
| Number of atoms of chlorine | In reactants (2HCl) | In products (AgCl) |
| Initially | 2 | 1 |
| To balance | 2 | 2 ×1 |
To equalise the number of chlorine atoms, we use 2 as the factor in the product AgCl. now the unbalanced equation becomes
Ag + 2HCl → 2AgCl + H2
Now count the atoms of each element on both sides of the equation, there is less number of silver atoms in the reactant. Now equalize the silver atoms, the balanced equation becomes
2Ag + 2HCl → 2AgCl + H2
Now indicate the physical states of the reactants and products
2Ag(s) + 2HCl(l) → 2AgCl ↓ + H2 ↑
d. H2SO4(aq) + NaOH(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + H2O(l)
Answer:
Step 1:
Rewrite the given equation as it is
H2SO4(aq) + NaOH(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + H2O(l)
Step 2:
write the number of atoms of each element in the unbalanced equation on both sides of the equation.
| Element | Number of atoms in reactants | Number of atoms in products |
| Na | 1 | 2 |
| S | 1 | 1 |
| O | 5 | 5 |
| H | 3 | 2 |
The number of oxygen atoms involved in different compounds on both sides (reactants and products) are equal. Therefore, balance the number of atoms of the second element, sodium.
Step 3:
To balance the number of sodium atoms:
| Number of atoms of sodium | In reactants | In products |
| To begin with | 1 (in NaOH) | 2 (in Na2SO4) |
| To balance | 1 × 2 | 2 |
To equalise the number of sodium atoms, we use 2 as the factor of NaOH in the reactants. Now, the partly balanced equation becomes as follows
H2SO4 + 2NaOH → Na2SO4 + H2O
Step 4:
Now, balance the number of hydrogen atoms:
| Number of atoms of hydrogen | In reactants | In products |
| To begin with | (in H2SO4) 2 (in NaOH) | 2 (in H2O) |
| To balance | 4 | 2 × 2 |
To equalise the number of hydrogen atoms, we use 2 as the factor or H2O in the products. The equation then becomes
H2SO4 + 2NaOH → Na2SO4 + H2O
Now, count the atoms of each element on both sides of the equation. The number of atoms on both sides are equal. Hence, the balanced equation is
H2SO4 + 2NaOH → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
Now indicate the physical states of the reactants and the products.
H2SO4(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
Question 8.
Identify the endothermic and exothermic reaction.
a. HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O + heat
Answer:
Exothermic reaction.
b. 2KClO3(s)⟶Δ2KCl(s)+3O2↑
Answer:
Exothermic reaction.
c. CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2 + heat
Answer:
Exothermic reaction.
d. CaCO3(s)⟶ΔCaO(s)+CO2↑
Answer:
Exothermic reaction.
Question 9.
Match the column in the following table:
| Reactants | products | Type of chemical reaction |
| BaCl2(aq) + ZnSO4(aq) | H2CO3(aq) | Displacement |
| 2 AgCl(s) | FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s) | Combination |
| CuSO4(aq) + Fe(s) | BaSO4↓ + ZnCl2(aq) | Decomposition |
| H2O(l) + CO2(g) | 2Ag(s) + Cl2(g) | Double displacement |
Answer:
| Reactants | products | Type of chemical reaction |
| BaCl2(aq) + ZnSO4(aq) | BaSO4↓ + ZnCl2(aq) | Double displacement |
| 2 AgCl(s) | 2Ag(s) + Cl2(g) | Decomposition |
| CuSO4(aq) + Fe(s) | FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s) | Displacement |
| H2O(l) + CO2(g) | H2CO3(aq) | Combination |