Question 1.
a. Alloy of sodium with mercury.
Answer: The alloy of sodium with mercury is Silver amalgam.
b. Molecular formula of common ore of aluminum.
Answer: Molecular formula of common ore of aluminium is Al2O3.nH2O.
c. The oxide that forms salt and water by reacting with both acid and base.
Answer: The oxide that forms salt and water by reacting with both acid and base is Aluminium oxide (Al2O3).
d. device used for grinding an ore.
Answer: A grinding mill is a device used for grinding an ore.
e. The nonmetal having electrical conductivity.
Answer: The nonmetal which has electrical conductivity is Graphite.
f. The reagent that dissolves noble metals.
Answer: The reagent that dissolves noble metals like gold and platinum is Aqua regia.
Question 2. Make pairs of substances and their properties.

Answer:
(1) Potassium bromide – Soluble in water
(2) Gold – High ductility
(3) Sulphur – Combustible
(4) Neon – No chemical reaction
Question 3. Identify the pairs of metals and their ores from the following.
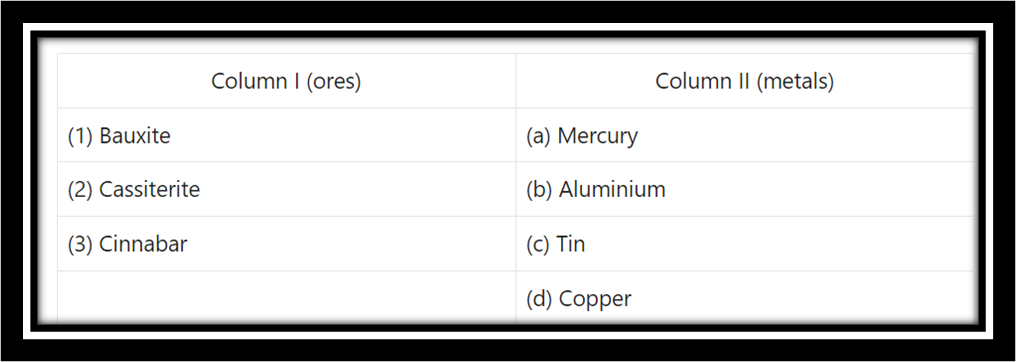
Answer:
(1) Bauxite – Aluminium
(2) Cassiterite – Tin
(3) Cinnabar – Mercury
Question 4. Explain the terms.
a. Metallurgy
Answer. Metallurgy is the process of extracting metals in their pure form from ores, followed by purifying the metals using various purification methods. This entire process is known as metallurgy.
b. Ores.
Answer: Ores are minerals from which metals can be extracted profitably and conveniently. Examples: Bauxite (Al2O3.H2O), Cinnabar (HgS).
c. Minerals.
Answer: Minerals are compounds of metals and impurities found naturally. Rocks consist of blends of minerals, with talc and granite being specific examples of minerals.
Examples: Rocks are composed of mixtures of minerals. Talc and granite are minerals.
d. Gangue.
Gangue is the term used to describe impurities such as soil, sand, and rocky material found in ores, which are metal compounds.
Question 5.
Write scientific reasons.
a. Lemon or tamarind is used for cleaning copper vessels turned greenish.
- Copper oxidizes in the air, creating black copper oxide. When exposed to carbon dioxide, copper oxide gradually reacts and develops a green layer, known as copper carbonate.
- Lemon and tamarind, which contain acid, dissolve the green film of basic copper carbonate found on the surface of a tarnished copper utensil, restoring its shine.
b. Generally the ionic compounds have high melting points.
Answer: Ionic compounds are solid and hard because of the strong attraction between oppositely charged ions. They have high intermolecular attraction, requiring a large amount of energy to overcome it. As a result, they possess high melting points.
c. Sodium is always kept in kerosene.
(OR)
Why is sodium stored in kerosene?
- Sodium reacts very strongly with oxygen in the air, causing it to ignite when exposed.
- It does not react with kerosene and will sink in it. Therefore, sodium is stored in kerosene to prevent accidental fires and protect it.
d. Pine oil is used in the froth floatation process.
Answer 1. When using the froth flotation process to concentrate an ore, the ore gets mixed with water and pine oil. Bubbling air through the mixture causes the formation of froth.
2. In this froth, the mineral particles in the ore, which are preferentially wetted by the oil, float to the top.
3. On the other hand, gangue particles, which are wetted by water, settle down. This separation allows for the concentration of the mineral from the gangue in the ore.
e. Anodes need to be replaced from time to time during the electrolysis of alumina.
- When alumina is electrolyzed, the oxygen released at the carbon anode combines with graphite rods to produce carbon dioxide.
- During the electrolysis of alumina, the anodes undergo oxidation and are consistently worn down. Therefore, it is crucial to periodically replace the anodes
Question 6. When a copper coin is dipped in silver nitrate solution, a glitter appears on the coin after some time. Why does this happen? Write the chemical equation.
Answer: Dipping a copper coin in a silver nitrate solution result in the copper displacing silver from the solution. The liberated silver then deposits onto the copper coin, forming a shiny silver coat on it.
Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
Question 7. The electronic configuration of metal ‘A’ is 2, 8, 1 and that of metal ‘B’ is 2, 8, 2. Which of the two metals is more reactive? Identify these metals. Write their reaction with dilute hydrochloric acid
Answer. If the number of electrons in the outermost orbit is less, then the metal is more reactive. Metal A contains one electron in the outermost shell, while metal B contains two electrons. Hence, metal A is more reactive than metal B.
Metal A is sodium and metal B is magnesium. Reactions Of Na and Mg with dil. HCI are
2Na +2HCI (aq) → 2NaCL(aq) + H2(g)
Sodium Sodium Hydrogen
Mg + 2HCI → Mgcl2 + H2 (g)
Magnesium dil.hcl Magnesium chloride Hydrogen
Question 8.
Draw a neat labelled diagram.
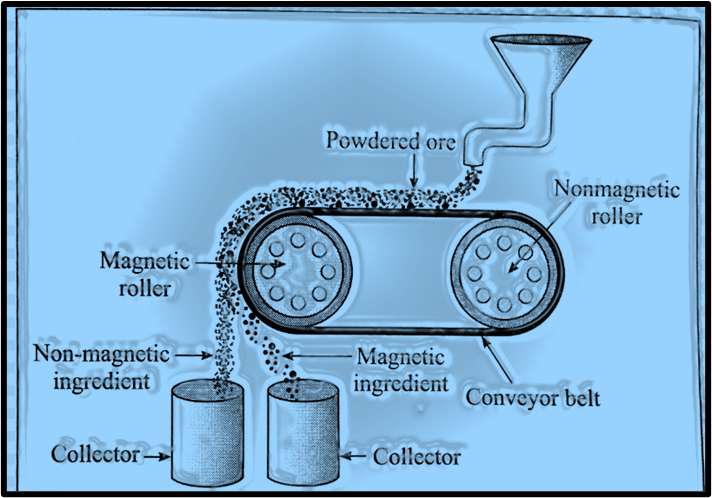
a. Magnetic separation method.
b. Forth floatation.
Answer:

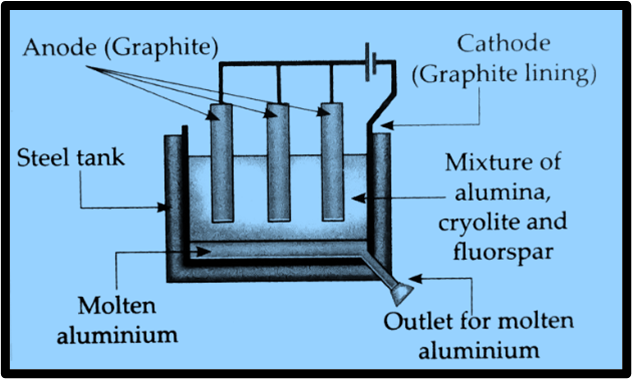
c. Electrolytic reduction of alumina.
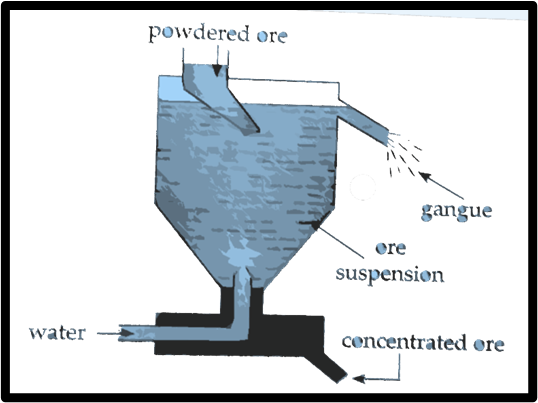
d. Hydraulic separation method.
Answer:
Question 9.
Write chemical equation for the following events.
a. Aluminium came in contact with air.
Aluminium is a highly reactive metal that is typically shielded from the air by a thin oxide layer on its surface. However, if this layer is disrupted, aluminum can react with oxygen in the air, resulting in a bright white flame and the formation of aluminum (III) oxide.
4Al +3O2 → 2Al2O3
b. Iron filings are dropped in aqueous solution of copper sulphate.
Answer: When iron filings are added to copper sulphate solution, the iron displaces copper from the solution. This results in the iron filings becoming coated with reddish-brown copper metal, while the blue color of the copper sulphate solution slowly fades and ferrous sulphate is produced.
Fe (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → FeSO4(aq) + CU(s)
(c) . A reaction was brought about between ferric oxide and aluminium.
Answer. When ferric oxide reacts with iron, it forms aluminium oxide and iron in an extremely exothermic thermite reaction. This process generates significant heat that melts oxygen and aluminium, making it valuable for welding machinery and manufacturing grenades in warfare.
The chemical reaction for the above is as follows:
3Fe3O2 + 4Al → 2Al2O3 + 6Fe
d. Electrolysis of alumina is done.
Answer. Aluminium is deposited at the cathode during the electrolysis of alumina. The heavier molten aluminium settles at the bottom of the tank due to its weight compared to the electrolyte. Oxygen gas is released at the anode.
Anode reaction: 2O–– → O2 + 4e– (Oxidation)
Cathode reaction: Al3 + 3e– → Al(l) (Reduction)
e. Zinc oxide is dissolved in dilute hydrochloric acid.
Answer: When zinc oxide is mixed with dilute hydrochloric acid, it produces zinc chloride and water.
ZnO + 2 HCl → ZnCl2 + H2O.
Question 10.
Complete the following statement using every given options.
During the extraction of aluminium
a. Ingredients and gangue in bauxite.
b. Use of leuching during the concentration of ore.
c. Chemical reaction of transformation of bauxite into alumina by Hall’s process.
d. Heating the aluminium ore with concentrated caustic soda.
Answer: c. Chemical reaction of transformation of bauxite into alumina by Hall’s process.
Question11. Divide the metals Cu, Zn, Ca, Mg, Fe, Na, Li into three groups, namely, reactive metals, moderately reactive metals and less reactive metals.
Answer: Reactive metals: Na, Li, Ca
Moderately reactive metals: Zn, Fe, Mg,
Less reactive metals: Cu