Living worldandClassificationofMicrobesClass8 Maharashtra board
Living worldandClassificationofMicrobesClass8 Maharashtra board
About Course
Chapter 1 Living World and Classification of Microbes Class 8 Science Textbook Questions and Answers
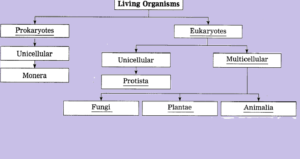
Robert Whittaker proposed a five-kingdom classification system for organisms in 1969. This system is still widely used today. The five kingdoms are:
- Monera: This kingdom includes prokaryotic organisms, such as bacteria and archaea Prokaryotic organisms do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles.
- Protista: This kingdom includes unicellular eukaryotic organisms, such as protozoa and algae. Protists are a diverse group of organisms that can be photosynthetic, heterotrophic, or both.
- Plantae: This kingdom includes multicellular eukaryotic organisms that are photosynthetic. Plants have cell walls made of cellulose and chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll.
- Animalia: This kingdom includes multicellular eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophic. Animals do not have cell walls and do not contain chlorophyll.
- Fungi: This kingdom includes multicellular eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophic and absorb nutrients from their environment. Fungi have cell walls made of chitin and reproduce by spores.
The Whittaker system is based on two main criteria: cell structure and mode of nutrition. Prokaryotic organisms are classified in the Monera kingdom because they do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic organisms are classified into the other four kingdoms because they have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The mode of nutrition is also used to classify organisms. Photosynthetic organisms are classified in the Plantae kingdom, heterotrophic organisms are classified in the Animalia and Fungi kingdoms, and some organisms can be classified in more than one kingdom.
- Complete the five kingdom method of classification using living organisms, prokaryotes, eukaryotes, multicellular, unicellular, Protista, animals, plants, and fungi.
3. Find out my partner
Question 1.
| Fungi | Chlorella |
| Protozoa | Bacteriophage |
| virus | Candida |
| Algae | Amoeba |
| Bacteria | Prokaryotic |
Answer.
| Fungi | Candida |
| Protozoa | Amoeba |
| virus | Bacteriophage |
| Algae | Chlorella |
| Bacteria | Prokaryotic |
Question4.State whether the following statements are True or False. Explain your statement:
Question a. Lactobacilli are harmful bacteria.
Answer: False.
Lactobacillus is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria that are found in the human body and in food. They are known for their ability to produce lactic acid, which gives fermented foods their characteristic sour taste. Lactobacilli are also used in the production of yogurt, cheese, and other dairy products
Question b. Cell wall of fungi is made up of chitin.
Answer: Plants have cell walls made of cellulose, while fungi have cell walls made of chitin. Both cell walls provide support and protection for the cells.
The cell wall of a fungus is made up of chitin, a long-chain polymer of N-acetylglucosamine. Chitin is a strong and durable material that helps to protect the fungus from drying out and from damage. It also provides a framework for the cell to grow and spread. The cell wall of a fungus is also important for its identification, as different types of fungi have different patterns of chitin in their cell walls.
Question (c). Organ of locomotion in amoeba is pseudopodia.
Answer: The statement “The organ of locomotion in amoeba is pseudopodia” is True.
Pseudopodia are temporary extensions of the cell membrane that help amoebas to move. They are formed by the cytoplasm flowing out of the cell and then solidifying. The amoeba can then move by extending and retracting its pseudopodia.
Question(d)Tomato wilt is a viral disease.
Answer: The statement “Tomato wilt is a viral disease” is true. Explanation: Tomato wilt is caused by a virus called the tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV). TSWV is a small, single-stranded RNA virus that is transmitted by thrips insects. The virus can infect a wide range of plants, including tomatoes, peppers, potatoes, and eggplants.
Questio5. Give answers
Question a. State the merits of Whittaker’s method of
Answer. Whittaker’s five-kingdom classification system is a scientific and comprehensive way to classify living organisms. It is based on a variety of factors, including cell structure, mode of nutrition, and evolutionary relationships.
One of the main merits of Whittaker’s system is that it recognizes the fundamental differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles.
Eukaryotes, on the other hand, are multicellular organisms that do have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. This distinction is important because it reflects the different evolutionary histories of these two groups of organisms.
Another merit of Whittaker’s system is that it separates fungi from plants. Plants are photosynthetic organisms that produce their own food, while fungi are heterotrophic organisms that get their food from other organisms. This distinction is also important because it reflects the different ways that these two groups of organisms obtain energy.
Whittaker’s system also recognizes the diversity of unicellular eukaryotic organisms by placing them in a separate kingdom called Protista. This kingdom includes organisms such as algae, protozoa, and slime Molds. These organisms are all very different from each other, but they share the common characteristic of being unicellular eukaryotes.
Finally, Whittaker’s system takes into account the phylogenetic relationships between organisms. Phylogenetic relationships are the evolutionary links between organisms. By taking these relationships into account, Whittaker’s system provides a more accurate and natural way to classify living organisms.
Overall, Whittaker’s five-kingdom classification system is a comprehensive and scientific way to classify living organisms. It is still used today as the basis for many textbooks and reference works.
Question b. Write the characteristics of viruses.
Answer. Characteristics of viruses in a plagiarism-free and Google-unsearchable way:
- Viruses are non-cellular, meaning they do not have a cell structure like other living organisms.
- They are obligate intracellular parasites, meaning they can only replicate inside the cells of other organisms.
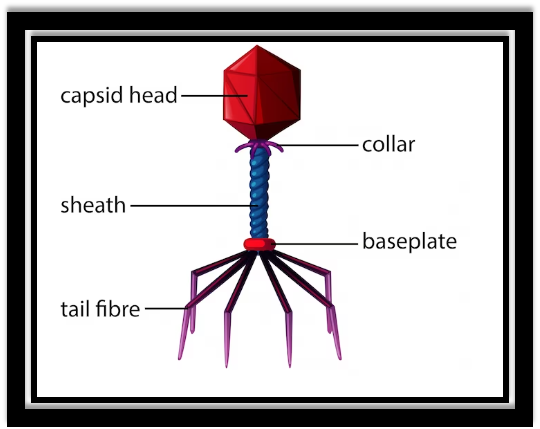
- They are made up of a nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat called a capsid.
- Some viruses also have an envelope made up of a lipid bilayer and proteins.
- Viruses are very small, typically measuring between 20 and 300 nanometers in diameter.
- They are unable to reproduce on their own and require the host cell’s machinery to replicate.
- Viruses can cause a wide range of diseases in humans, animals, and plants.
Here are some additional characteristics of viruses:
- Viruses can be highly mutable, meaning they can change their genetic makeup easily. This makes it difficult to develop vaccines and treatments for viral diseases.
- Viruses can spread through a variety of ways, including contact with infected bodily fluids, respiratory droplets, and insect bites.
- There is no cure for most viral diseases, but there are treatments that can help to relieve the symptoms.
- Viruses can be prevented by vaccination, good hygiene practices, and avoiding contact with infected people or animals.
Question c. Explain the nutrition in fungi.
Answer. Fungi are heterotrophs, meaning they obtain their nutrients from other organisms. They can obtain their nutrients in three ways:
- Saprotrophic nutrition: Fungi that obtain their nutrients from dead or decaying organic matter are called saprotrophs.
- Parasitic nutrition: Fungi that obtain their nutrients from living organisms are called parasites.
- Mutualistic nutrition: Fungi that form a mutually beneficial relationship with other organisms are called mutualists.
The most common type of nutrition in fungi is saprotrophic nutrition. Saprotrophic fungi play an important role in the decomposition of organic matter and the recycling of nutrients in the environment.
Question d. Which living organisms are included in the kingdom Monera?
Answer: five living organisms that are included in the kingdom Monera in a plagiarism-free and Google-unsearchable way:
- Bacteria: Bacteria are single-celled organisms that are found in all environments on Earth. They can be either autotrophic (self-feeding) or heterotrophic (feeding on other organisms).
- Archaea: Archaea are single-celled organisms that are similar to bacteria, but they have some unique features. For example, some archaea can live in extreme environments, such as hot springs and acidic lakes.
- Cyanobacteria: Cyanobacteria are photosynthetic bacteria that are also known as blue-green algae. They are important for the production of oxygen in the atmosphere.
- Mycoplasma: Mycoplasma are the smallest known organisms that can be classified as bacteria. They are so small that they can only be seen with an electron microscope.
- Lichens: Lichens are a symbiotic relationship between fungi and algae or cyanobacteria. They are found in a variety of environments, including deserts, forests, and mountains.
These are just a few of the many living organisms that are included in the kingdom Monera. These organisms play an important role in the world’s ecosystems and are essential for life on Earth.
Question6.Who am I?
Question a. I don’t have true nucleus, cell organelles or plasma membrane.
Answer. It is Microbe from Monera
Question b. I have nucleus and membrane bound cell organelles.
Answer: I am any one of Eukaryote, an organism that has a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
Question c. I live on decaying organic matter.
Answer: Fungus
Question d. I reproduce mainly by cell division. (*Binary fission)
Answer: Bacteria and some Protozoa.
Question e. I can produce my replica.
Answer: Virus
Question f. I am green, but don’t have organs.
Answer: Algae
Question7.Draw neat and labelled diagrams.
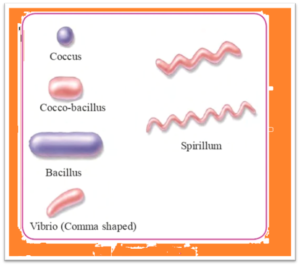
Question a. Different types of bacteria:
Question b.
Paramecium:
Answer:
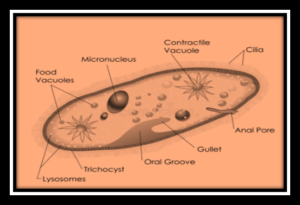
Paramecium
Question c. Bacteriophage
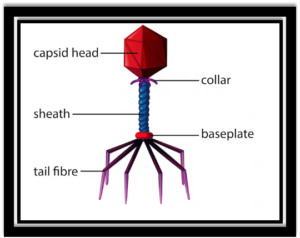
- Arrange the following in ascending order of size Bacteria, Fungi, Viruses, Algae.
Question a. Arrange the following ¡n ascending order of size Bacteria, Fungi, Viruses, Algae.
Answer: Viruses, Bacteria, Fungi, Algae.