II. SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What are good and poor conductors of electricity?
Answer:
Good conductors of electricity allow electric current to pass through them. Examples: copper, aluminium, iron, silver.
Poor conductors (insulators) do not allow current to pass easily. Examples: plastic, rubber, wood, glass.
2. What do you understand by hydrolysis of water?
Answer:
Hydrolysis of water means breaking water into hydrogen and oxygen by passing an electric current through it. This is also called the electrolysis of water.
3. What is the difference between a cathode and an anode?
Answer:
A cathode is the negative electrode where positive ions move.
An anode is the positive electrode where negative ions move.
4. What is chemical effect of electricity?
Answer:
The chemical effect of electricity is the process in which electric current causes a chemical change in a solution. This may include gas release, color change, or metal deposition.
5. What is electroplating? Which metal is electroplated on iron to prevent it from rust?
Answer:
Electroplating is the process of coating one metal with another metal using electricity.
Zinc is electroplated on iron to prevent rusting. This process is also called galvanization.
6. Electroplating is hazardous to the environment. Give reason.
Answer:
Electroplating is hazardous because it produces toxic chemicals, metal-laden wastewater, and harmful acids. If these are released into water bodies, they pollute soil and water and harm living organisms.
III. LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. How would you show that pure water does not conduct electricity?
Answer:
To show this, take a circuit with a bulb, battery, and connecting wires.
Pour pure distilled water in a beaker and dip the wire ends into it.
The bulb does not glow, proving that pure water does not conduct electricity because it has no salts or minerals.
If you add a little salt, the bulb glows, showing that impure water conducts electricity.
2. What is an LED? How is it better than an ordinary bulb?
Answer:
An LED (Light Emitting Diode) is a small device that glows when electric current passes through it.
It is better than an ordinary bulb because:
- It uses very little electricity
- It does not produce much heat
- It lasts much longer
- It can work with low voltage
3. Why is it dangerous to handle electrical appliances with wet hands?
Answer:
It is dangerous because water contains dissolved salts that make it a good conductor. When hands are wet, electricity can pass easily through the body and cause electric shock. So appliances should always be handled with dry hands.
4. How would you electroplate an iron spoon with copper? Describe with a diagram.
Answer:
To electroplate an iron spoon with copper:
- Take a beaker filled with copper sulphate solution.
- Connect the iron spoon to the negative terminal of a battery (cathode).
- Connect a copper plate to the positive terminal (anode).
- When electricity passes, copper ions from the solution deposit on the iron spoon.
- After some time, the spoon gets a shiny copper coating.
Battery (+) —- Copper Plate (Anode)
Battery (-) —- Iron Spoon (Cathode)
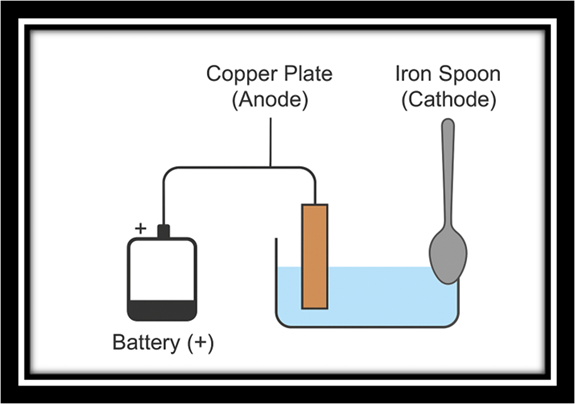
Beaker filled with Copper Sulphate Solution
5. What are the industrial uses of electroplating?
Answer:
Electroplating is widely used in industries for:
- Preventing rust on iron objects
- Making jewellery shiny with gold or silver coating
- Improving appearance of bathroom fittings and car parts
- Protecting metals from corrosion
- Increasing durability of tools and machine parts
IV. HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS
1. Rainwater is considered as the purest form of water, but still it can conduct electricity. Why?
Answer:
Rainwater can conduct electricity because it dissolves dust, gases, and minerals from the atmosphere. These impurities contain ions, which help electricity pass through it. So, rainwater is not completely pure.
2. How does electroplating help to control monetary loss?
Answer:
Electroplating reduces monetary loss by:
- Making metals last longer
- Preventing rust and damage
- Reducing the need for frequent replacement
- Allowing cheap metals to be coated with costly metals, making products affordable
This saves money in industries and for consumers.