1. Complete the statement by filling the gaps using appropriate term from the terms given in the bracket. (slow, coloured, arrow, fast, smell, milky, physical, product, chemical, reactant, covalent, ionic, octet, duplet, exchange, sharing, equality sign)
a. An ……………. is drawn in between the reactants and products while writing the equation for a chemical reaction.
Answer. An arrow is drawn in between the reactants and products while writing the equation for a chemical reaction.
b. Rusting of iron is a ………………… chemical change.
Answer. Rusting of iron is a slow chemical change.
c. The spoiling of food is a chemical change which is recognized from the generation of certain ………… due to it.
Answer. The spoiling of food is a chemical change which is recognized from the generation of certain smell due to it.
d. A colourless solution of calcium hydroxide in a test tube turns ….. on blowing in it through a blow tube for some time.
Answer. A colourless solution of calcium hydroxide in a test tube turns milky on blowing in it through a blow tube for some time.
e. The white particles of baking soda disappear when put in lemon juice. This means that it is a ………. change.
Answer. The white particles of baking soda disappear when put in lemon juice. This means that it is a chemical change
f. Oxygen is a …………….. in respiration.
Answer. Oxygen is a reactant in respiration.
g. Sodium chloride is ……….. compound while hydrogen chloride is ……… compound.
Answer. g. Sodium chloride is ionic compound while hydrogen chloride is covalent compound.
h. Electron ……… is complete in each hydrogen in a hydrogn molecule.
Answer. Electron duplet is complete in each hydrogen in a hydrogen molecule.
i. Chlorine (Cl2 ) molecule is formed by …………… of electrons between two chlorine atoms.
Answer. Chlorine (Cl₂) molecule is formed by sharing of electrons between two chlorine atoms.
2. Explain by writing a word equation.
a. Respiration is a chemical change.
- Word Equation: Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
- Explanation: During respiration, glucose and oxygen react inside our cells to produce new substances—carbon dioxide, water, and energy. This irreversible formation of new products confirms it is a chemical change.
b. Hard water gets softened on mixing with washing soda.
- Word Equation: Calcium ions (in hard water) + Sodium carbonate (washing soda) → Calcium carbonate (precipitate) + Sodium ions
- Explanation: The calcium ions causing hardness react with washing soda to form solid calcium carbonate, which settles out. This removal of calcium ions through a chemical reaction softens the water.
c. Lime stone powder disappears on adding to dilute hydrochloric acid.
- Word Equation: Calcium carbonate (limestone) + Hydrochloric acid → Calcium chloride + Water + Carbon dioxide gas
- Explanation: The acid reacts with the limestone, dissolving it and producing new substances. The fizzing (carbon dioxide gas) and formation of a soluble salt (calcium chloride) make the powder “disappear,” indicating a chemical change.
d. Bubbles are seen on adding lemon juice to baking soda.
- Word Equation: Citric acid (in lemon juice) + Sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) → Sodium citrate + Water + Carbon dioxide gas
- Explanation: The acid and baking soda react vigorously in a neutralization reaction. The bubbles are carbon dioxide gas, a new product, proving a chemical change is occurring.
3. Match the pairs.
| a. Photosynthesis | i. Tendency to lose electrons |
| b. Water | ii. Reactant in combustion |
| c. Sodium chloride | iii. Chemical change |
| d. Dissolution | iv. Covalent bond of salt in water |
| e. Carbon | v. Ionic bond |
| f. Fluorine | vi. Physical change |
| g. Magnesium | vii. Tendency to form anion |
| Group A | Group B |
| a. Photosynthesis | iii. Chemical change |
| b. Water | iv. Covalent bond |
| c. Sodium chloride | v. Ionic bond |
| d. Dissolution of salt in water | vi. Physical change |
| e. Carbon | ii. Reactant in combustion |
| f. Fluorine | vii. Tendency to form anion |
| g. Magnesium | i. Tendency to lose electrons |
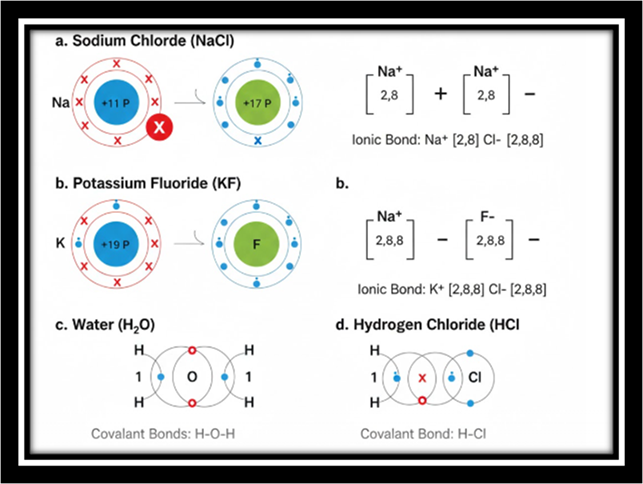
4. Show with the help of diagram of electronic configuration how the following compound are formed from the constituent atoms.
a. Sodium chloride
b. Potassium fluoride
c. Water
d. Hydrogen chloride